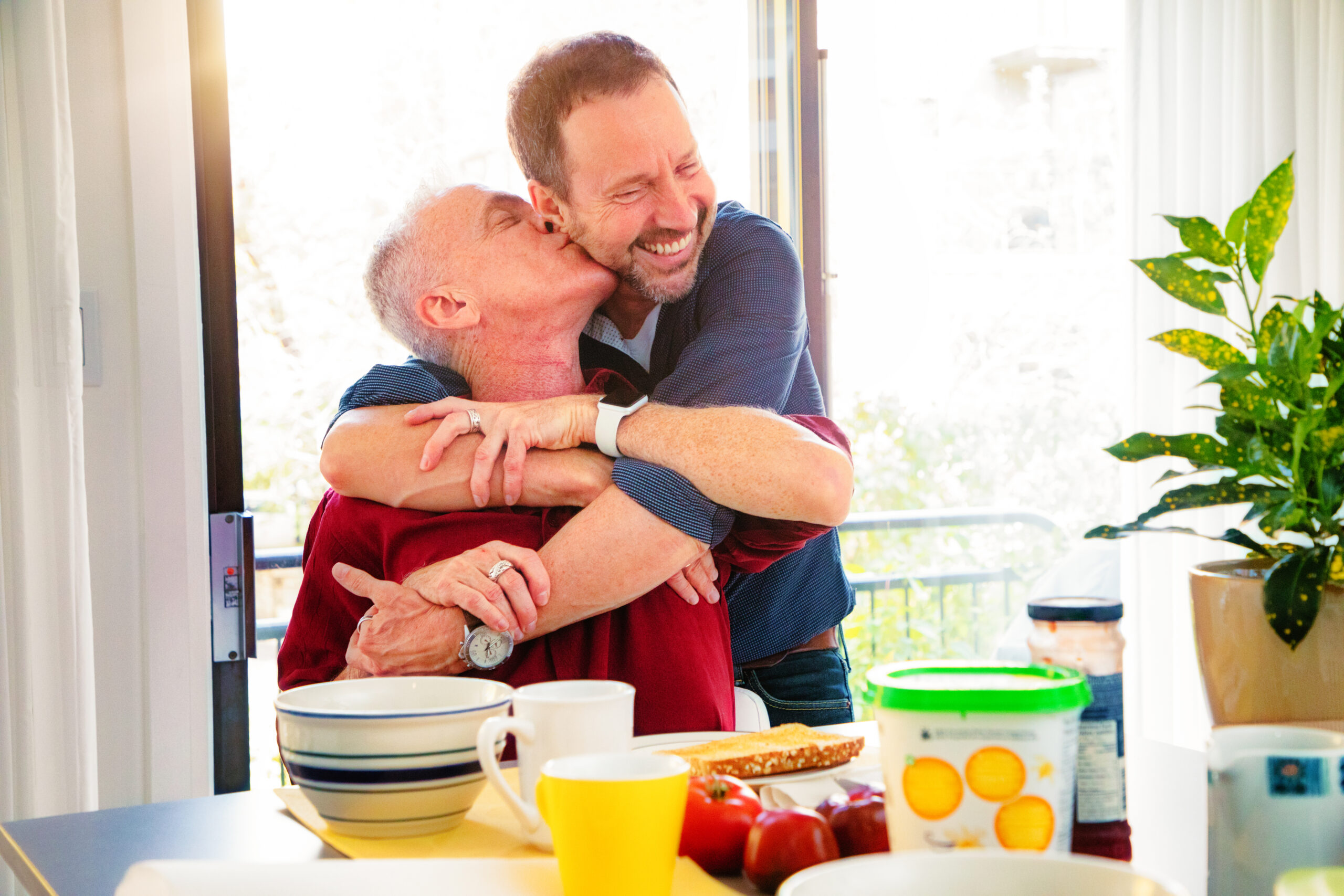
Scientists have been studying addiction since the 1930s, and their discoveries have transformed how we understand and treat substance use disorder (SUD). Thanks to decades of research, addiction is now recognized as a chronic brain disease, allowing for evidence-based treatments that address all aspects of addiction. [National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).]
How Science Defines Addiction
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) defines addiction as a chronic, relapsing brain disease characterized by compulsive drug use despite harmful consequences. Addiction affects brain structure and function, impacting self-control and decision-making. [NIDA].
The Science Behind Addiction and the Brain
Decades of research prove that addiction is not just about willpower. It is a complex disease that rewires the brain’s reward system. [NIDA].
Substance use affects neurotransmitters like dopamine, which controls feelings of pleasure and motivation.
Over time, the brain adapts, making it harder to feel them from natural rewards, leading to compulsive drug-seeking behavior.
Because addiction affects both the brain and behavior, treatment must take a holistic approach that addresses psychological, and biological, and social factors. [CDC].
Evidence-Based Addiction Treatment
Science has played a key role in shaping modern addiction treatment, moving away from one-size-fits-all models to a more personalized, data-driven approach to care. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration emphasizes the importance of integrating medications with therapies to provide a comprehensive treatment plan. [SAMHSA]
Is Addiction Curable?
One of the biggest misconceptions about addiction is that it can be permanently cured. Addiction is a chronic disease – similar to diabetes or hypertension – that can be managed effectively but not eliminated entirely. [CDC] While researchers continue to explore potential cures, current treatments focus on long-term recovery rather than a one-time fix.
Because addiction rewires brain chemistry, ongoing treatment and support are necessary to help individuals maintain sobriety and improve their quality of life. [NIDA]
Four Key Principles of Evidence-Based Treatment:
- Personalized Treatment Plans: No single treatment plan works for everyone. Individual care plans ensure that each person receives the therapies and support that best fit their needs.
- Behavioral Therapies: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and other techniques help people recognize triggers and change unhealthy thought patterns.
- Co-Occurring Disorders: Treating both addiction and mental health disorders like anxiety, depression, or PTSD leads to better outcomes. [SAMHSA]
- Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT): Medications like naltrexone or buprenorphine can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Why a Holistic Approach Matters
Effective addiction treatment does not just focus on stopping substance use. It focuses on building a strong foundation for life-long recovery. Addressing mental health and emotional wellbeing help address the underlying causes of addiction and encourages long-term success.
Start Your Recovery Journey Today
At EOSIS, we use evidence-based treatment methods to support recovery. Whether in a residential or outpatient setting, we provide comprehensive addiction care across the Twin Cities.